Solar power represents one of humanity’s most promising renewable energy sources. The sun provides more energy in a single hour than the world uses in an entire year. Understanding how this abundant resource can be harnessed effectively is crucial as we move toward a more sustainable energy future.
Basic Principles
Solar energy conversion begins with solar radiation striking specialized materials that can convert light into usable forms of energy. The photovoltaic effect, discovered in 1954 at Bell Labs, forms the foundation of modern solar power generation. When sunlight strikes a semiconductor material like silicon, it releases electrons, creating an electric current that can be captured and utilized.
The process involves multiple layers of specially treated materials working together. Silicon wafers are typically sandwiched between layers of boron and phosphorus, creating positive and negative charges that facilitate electron movement when exposed to sunlight. This fundamental process enables both direct electricity generation and indirect applications like solar heating.
Solar Technologies
Two technologies dominate the solar energy landscape: photovoltaic (PV) systems and solar thermal systems. PV panels convert sunlight directly into electricity through semiconductor materials, typically silicon-based cells arranged in panels of 60, 72, or 90 cells each. These systems can range from small residential installations to massive utility-scale solar farms.
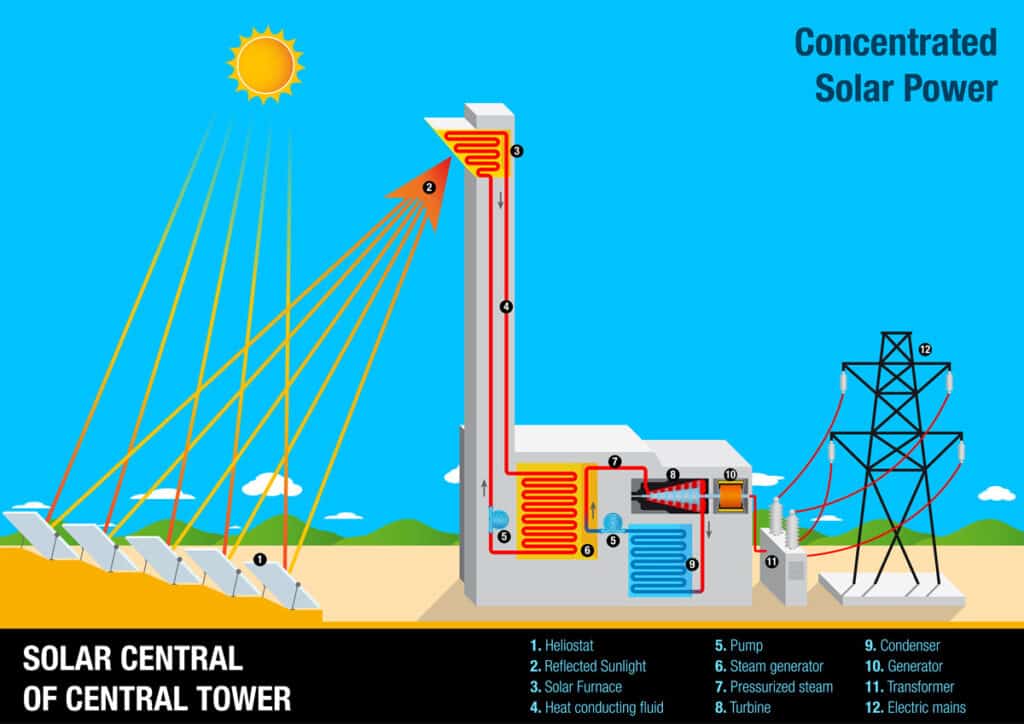
Solar thermal systems, by contrast, focus on heat collection and transfer. These systems can provide hot water for domestic use, process heat for industrial applications, or drive steam turbines in large-scale power plants. The technology varies from simple rooftop water heaters to sophisticated concentrated solar power plants using mirrors to focus sunlight.
Power Generation Process
The power generation process in PV systems begins when photons strike the solar panel surface. This interaction causes electrons to be released within the semiconductor material, creating an electric current. This direct current (DC) electricity is then converted to alternating current (AC) through inverters, making it compatible with standard electrical systems.
Modern solar installations often include sophisticated monitoring and control systems that optimize power generation and distribution. These systems can track the sun’s position, adjust for weather conditions, and manage power flow to maximize efficiency and reliability.

Applications and Scale
Solar power applications range from small calculator cells to massive utility-scale installations covering hundreds of acres. Residential systems typically mount on rooftops, providing household electricity and often feeding excess power back to the grid through net metering arrangements. Commercial installations can power entire buildings or industrial complexes, while utility-scale solar farms generate power for thousands of homes.
Solar technology’s flexibility allows for various implementation strategies, from grid-tied systems that supplement traditional power sources to completely off-grid solutions for remote locations. Hybrid systems combining solar with other renewable or traditional power sources offer increased reliability and efficiency.
Environmental Benefits
Solar power has significant environmental benefits. Solar power systems produce no emissions or pollutants during operation, making them one of the cleanest energy sources available. The carbon footprint of manufacturing solar panels continues to decrease as production becomes more efficient and materials are increasingly recycled.
Modern solar installations can operate for 25 years or more with minimal environmental impact, providing clean, renewable energy throughout their lifetime. This long-term sustainability makes solar power a crucial component in efforts to reduce carbon emissions and combat climate change.
Future Developments
The solar energy sector continues to evolve rapidly, with ongoing improvements in efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Research into new materials and manufacturing techniques promises to reduce costs further while increasing power output. Advanced storage solutions, including improved battery technologies, are addressing the intermittent nature of solar power.
Integration with smart grid technologies is enabling better management of solar resources, while innovations in panel design and installation are making solar power more accessible and efficient. These developments suggest a bright future for solar energy as a primary power source in our sustainable energy landscape.











Leave a Reply