Understanding the technology behind solar powered generators requires a thorough grasp of inverter technology, which serves as the crucial bridge between solar power collection and usable electricity. This comprehensive guide explores how inverters enable solar generators to provide reliable power for various applications, from home backup systems to emergency response solutions.
Basic Function and Purpose
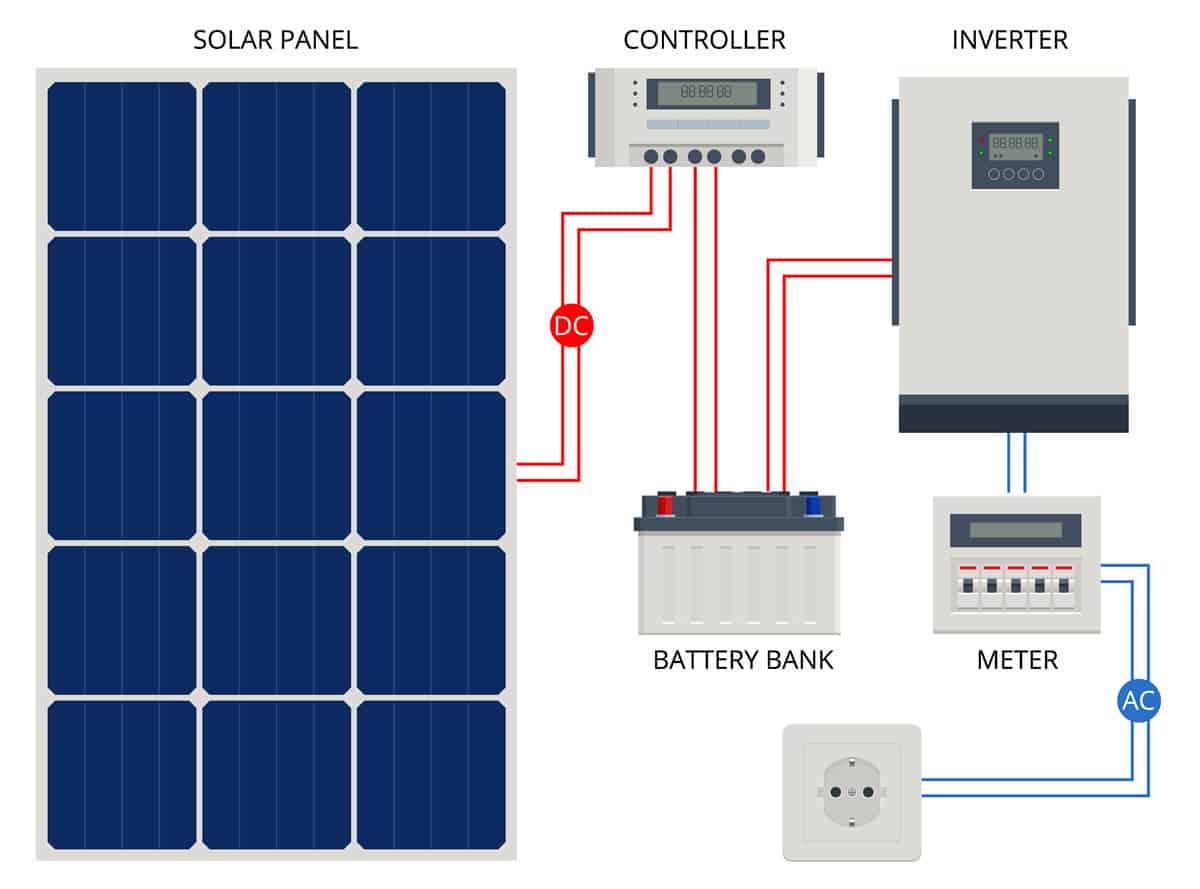
At its core, an inverter’s primary function is converting direct current (DC) produced by solar panels into alternating current (AC) that powers household appliances. When exploring whether solar generators can really power an entire house, the inverter’s capacity and efficiency become critical factors. Modern inverters not only convert power but also regulate voltage and frequency while ensuring power quality meets utility standards.
The complexity of this conversion process requires sophisticated electronic systems that can maintain stable output under varying input conditions. This capability becomes particularly important when dealing with fluctuating solar input or varying load demands, ensuring consistent power delivery regardless of external conditions.
Types of Inverters
Pure sine wave inverters represent the gold standard in power conversion technology. These sophisticated devices produce clean, utility-grade power that’s compatible with sensitive electronics and medical equipment. This capability makes them particularly valuable for solar generators in disaster relief situations, where reliable power quality is essential for critical equipment.
Modified sine wave inverters offer a more economical solution for basic power needs. While they may not provide the same power quality as pure sine wave models, they can effectively run many common household appliances. Understanding solar power and solar energy applications helps determine which inverter type best suits specific needs. The choice between these types often depends on the intended application and budget constraints.
Key Components
Modern inverters incorporate several sophisticated components working in harmony to ensure reliable power conversion. Advanced power transistors handle the actual switching process, while microprocessor-controlled circuits ensure precise operation and optimal efficiency. Comprehensive filtering systems clean the output power, removing unwanted harmonics and ensuring stable voltage delivery.
Protection mechanisms play a crucial role in modern inverter design, safeguarding both the inverter and connected equipment from potential damage. These systems monitor various parameters including current, voltage, and temperature, responding instantly to any abnormal conditions that could compromise system integrity.
Performance Factors
Inverter performance depends on various factors that affect overall system efficiency. Temperature management plays a crucial role, as heat can significantly impact conversion efficiency. Modern units include sophisticated cooling systems and thermal protection to maintain optimal performance under varying conditions.
The efficiency of power conversion directly affects the overall performance of solar generator systems. Higher efficiency means more of the captured solar energy becomes usable power, reducing waste and improving system economics. Modern inverters typically achieve efficiency ratings above 90%, with some premium models exceeding 95%.
Advanced Features
Today’s inverters incorporate sophisticated features like Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) to optimize solar panel output. This technology continuously adjusts operating parameters to extract maximum power from solar panels under varying conditions. Smart monitoring capabilities allow users to track performance and identify potential issues before they become problems, while grid synchronization features enable seamless integration with existing power systems.
The integration of advanced monitoring and control systems has revolutionized inverter operation. These systems provide real-time performance data, enabling proactive maintenance and optimal system operation. Many modern inverters also include remote monitoring capabilities, allowing users to track system performance from anywhere with internet access.
Selection Criteria
Choosing the right inverter requires careful consideration of multiple factors that affect both initial performance and long-term reliability. Power requirements must be carefully matched to intended applications, while compatibility with existing systems ensures smooth integration. Efficiency ratings and power loss characteristics significantly impact operating costs, making them crucial considerations in system design.
Initial and long-term costs play a major role in inverter selection, but shouldn’t be the only determining factor. Reliability and warranty coverage provide important protection for your investment, while future expandability might be important for growing power needs.
Maintenance and Care
Regular maintenance ensures optimal inverter performance and longevity throughout the system’s life. Monthly performance monitoring helps identify trends that might indicate developing issues, while regular cleaning of cooling systems prevents temperature-related problems. Prompt attention to warning indicators can prevent minor issues from becoming major failures.
Professional inspection schedules should be maintained according to manufacturer recommendations, typically annually or semi-annually depending on usage patterns. These inspections can identify potential issues before they affect system performance, ensuring reliable operation when power is needed most.
Understanding these aspects of inverter technology helps ensure optimal performance and reliability in solar generator systems, whether for home backup power or emergency response applications. The continued evolution of inverter technology promises even greater efficiency and reliability in future systems, making solar power an increasingly attractive option for various applications.










Leave a Reply