Choosing between a propane and a gas generator can be crucial for homeowners, outdoor enthusiasts, and professionals alike.
Each type of generator has its own set of advantages and drawbacks, making the selection process more nuanced than it might initially appear.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the key differences between propane and gas generators, helping you decide based on your needs, budget, and environmental considerations.
Key Takeaways
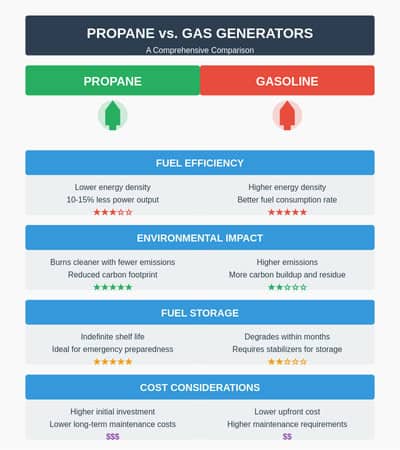
- Fuel Efficiency: Gas generators generally offer better fuel efficiency, consuming less fuel per hour of operation than propane generators.
- Environmental Impact: Propane generators burn cleaner, producing fewer emissions and reducing your carbon footprint.
- Fuel Storage: Propane has an indefinite shelf life, making it ideal for long-term storage, while gasoline can degrade within months.
- Initial Cost: Gas generators typically have a lower upfront cost, but propane generators may offer long-term savings through reduced maintenance.
- Performance: Gas generators often provide more power output, while propane generators offer better cold-weather starting and high-altitude performance.
- Availability: Gasoline is more widely available, but propane’s long shelf life makes it a better choice for emergency preparedness.
- Maintenance: Propane generators require less maintenance due to cleaner combustion and fewer carbon deposits.
By considering these factors alongside your specific requirements, you’ll be better equipped to choose the generator that best suits your needs.
The following sections will explore these aspects in greater detail, providing a comprehensive understanding of propane and gas generators.
Quick Comparison
| Generator Type | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Gasoline Generators |
|
|
| Propane Generators |
|
|
Understanding Generator Fuels
Before diving into the comparison, it’s essential to understand the fundamental properties of gasoline and propane as generator fuels.
Gasoline is a liquid petroleum derivative that’s widely available and has been the go-to fuel for portable generators for decades. It’s energy-dense and familiar to most users, making it a popular choice for gas generators. However, gasoline has a relatively short shelf life and can degrade over time, potentially causing issues with generator performance if not properly stored or used.
On the other hand, propane is a liquefied petroleum gas stored in pressurized tanks. It burns cleaner than gasoline and has an indefinite shelf life, making it an attractive option for those who don’t use their generators frequently. Propane is also less prone to fuel system clogging and carburetor issues, which can be common problems with gasoline generators.
Performance Comparison
When it comes to power output, gasoline generators typically have a slight edge. Propane has a lower energy density than gasoline, meaning a propane generator may produce about 10-15% less power than an equivalent gasoline model. However, this difference is often negligible for most residential and recreational applications.
Efficiency and fuel consumption rates can vary depending on the specific generator model and load conditions. Generally, propane generators tend to consume fuel at a slightly higher rate than gasoline generators. However, propane’s cleaner-burning nature can lead to less engine wear and potentially longer engine life.
Propane generators often have an advantage in cold weather conditions. Propane vaporizes at extremely low temperatures, making it easier to start a propane generator in cold weather than a gasoline generator, which may struggle with fuel thickening or carburetor icing.
For a detailed explanation of how generators work and their load capacities, check out our article on the basics of portable generators and portable generators load capacity.
Environmental Impact
One of the most significant advantages of propane generators is their lower environmental impact. Propane burns cleaner than gasoline, producing fewer emissions and pollutants. This reduces the generator’s carbon footprint and leads to better air quality around the generator during operation.
Propane’s cleaner combustion also means less carbon buildup in the engine, contributing to longer engine life and potentially lowering maintenance requirements over time.
Fuel Availability and Storage
Gasoline is widely available at gas stations, making it easily accessible in most situations. However, during power outages or natural disasters, gas stations may be closed or experience long lines.
While propane is not as ubiquitous as gasoline, it is still readily available at many hardware stores, gas stations, and dedicated propane suppliers. Propane’s key advantage is its indefinite shelf life. Unlike gasoline, which can degrade within months, properly stored propane can last for years without losing its effectiveness.
Propane has a clear advantage in terms of safety and longevity when it comes to storage. Propane tanks are designed for long-term storage and don’t pose the same fire hazards as stored gasoline. This makes propane an excellent choice for portable power for disaster preparedness.
Cost Analysis
The initial investment for a propane generator is often slightly higher than for a comparable gasoline model. However, propane’s cleaner burning nature and potential for less frequent maintenance can lower its long-term operational costs.
Fuel costs can fluctuate, but historically, propane has been competitively priced with gasoline on a per-energy-unit basis. Propane’s indefinite shelf life can also lead to cost savings, as you won’t need to periodically replace stored fuel.
Maintenance and Longevity
Propane generators typically require less frequent maintenance than their gasoline counterparts. The clean-burning nature of propane results in less carbon buildup and deposits in the engine, which can translate to fewer oil changes and less frequent servicing.
While generally reliable, gasoline generators may require more attention to fuel system maintenance, including regular carburetor cleaning and fuel stabilizer use for stored gasoline. For tips on maintaining your generator, regardless of fuel type, check out our generator maintenance guide.
Safety Considerations
Both propane and gasoline generators require careful handling and operation. Gasoline is highly flammable and poses fire and explosion risks if not stored or handled properly. While also flammable, propane is stored in pressurized tanks designed for safety.
Proper ventilation is crucial for both types of generators to prevent carbon monoxide buildup. Always operate generators outdoors and away from windows, doors, and vents. For more information on safe generator operation, read our article on portable power safety.
Versatility and Applications
Both propane and gasoline generators offer versatility for various applications:
- Residential backup power.
- Recreational use (camping, RVs, tailgating).
- Construction and job site power.
- Emergency and disaster relief.
The choice between propane and gasoline often comes down to specific needs and preferences. For example, propane might be preferred for long-term storage and cleaner operation, while gasoline might be chosen for its wider availability and slightly higher power output.
Dual-Fuel Generators: The Best of Both Worlds?
Dual-fuel generators offer an attractive solution for those who want the benefits of both fuels. These generators can run on either propane or gasoline, providing flexibility and convenience. Models like the DuroMax XP13000EH offer this dual-fuel capability, allowing users to switch between fuels based on availability or preference.
Making the Right Choice
When deciding between a propane and gas generator, consider the following factors:
- Your specific power needs and usage frequency
- Fuel availability in your area
- Storage capabilities and local regulations
- Environmental concerns
- Long-term cost considerations
- Maintenance preferences
Remember also to consider proper generator grounding for safe operation. Our guide on how to ground a generator provides essential information on this topic.
Conclusion
Choosing between a propane and a gas generator ultimately depends on your specific needs, circumstances, and priorities. Both types of generators have their strengths and weaknesses, and understanding these can help you make an informed decision.
Gas generators offer advantages in terms of fuel efficiency, power output, and initial cost. They’re an excellent choice for those who need a powerful, readily available solution and don’t mind more frequent maintenance. However, they come with drawbacks such as fuel degradation, higher emissions, and potential fuel spillage concerns.
On the other hand, propane generators shine in areas of fuel storage, cleaner emissions, and ease of maintenance. They’re ideal for those prioritizing long-term storage, environmental impact, and operation in extreme conditions. While they may have a higher upfront cost and lower fuel efficiency, the long-term benefits can outweigh these initial drawbacks for many users.
Consider your specific use case carefully:
- For emergency home backup, propane’s long shelf life makes it an attractive option.
- For construction sites or frequent use, a gas generator’s power and efficiency might be more suitable.
- Propane’s cleaner burn could be the deciding factor for environmentally conscious users or those in areas with strict emissions regulations.
Remember, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution. Weigh the pros and cons, consider your budget, fuel availability, and intended use. Don’t hesitate to consult with a professional if you’re unsure. With the right choice, you’ll ensure reliable power when you need it most, whether it’s for your home, work, or recreational activities.
Whichever type you choose, always prioritize safety, follow manufacturer guidelines, and perform regular maintenance to keep your generator running smoothly for years to come.
For those interested in exploring other fuel options, our article on portable generators: gas vs diesel provides additional insights into alternative fuel choices for generators.
FAQ
How do propane and gas generators compare in terms of fuel efficiency?
Propane generators are generally less fuel-efficient than gas generators. Gas generators typically consume about 0.75 gallons of fuel per hour at 50% load, while propane generators use approximately 1-2 pounds per hour at the same load. However, it’s important to note that fuel efficiency can vary depending on the specific model and operating conditions.
What are the main advantages of using a propane generator over a gas generator?
Propane generators offer several advantages over gas generators:
- Cleaner burning: Propane produces fewer emissions and is more environmentally friendly.
- Longer shelf life: Propane can be stored indefinitely without degradation, unlike gasoline which can go bad in as little as a month.
- Quieter operation: Propane generators tend to run more quietly than gas generators.
- Less maintenance: Propane generators require less frequent oil changes and have fewer carbon deposits.
Are there any safety considerations when choosing between propane and gas generators?
Both propane and gas generators have safety considerations, but they differ slightly:
- Propane is non-toxic and doesn’t spill, reducing the risk of ground contamination.
- Gas generators require more careful handling due to the flammability of gasoline and the potential for spills.
- Propane tanks are pressurized, which requires proper storage and handling to prevent leaks.
- Both types of generators should be operated outdoors to prevent carbon monoxide buildup.
Always follow manufacturer guidelines and local regulations for safe operation and storage of either type of generator.
How do the initial and long-term costs compare between propane and gas generators?
The cost comparison between propane and gas generators involves several factors:
- Initial purchase: Gas generators are generally less expensive upfront.
- Fuel costs: Gas is typically cheaper per unit of energy, but prices can fluctuate more than propane.
- Maintenance: Propane generators often have lower maintenance costs due to cleaner burning fuel.
- Lifespan: Propane generators may last longer due to less engine wear, potentially offsetting the higher initial cost.
Consider your specific usage patterns and local fuel prices when evaluating long-term costs.
Can I convert my gas generator to run on propane?
Yes, it is possible to convert many gas generators to run on propane using conversion kits. These kits typically include:
- A regulator to control propane flow
- An adapter to connect the propane tank
- A carburetor or fuel mixer modification
However, converting a generator may void its warranty and could affect its performance. It’s crucial to use a kit specifically designed for your generator model and have the conversion done by a qualified technician to ensure safety and proper operation.
How do propane and gas generators perform in extreme weather conditions?
Propane and gas generators perform differently in extreme weather:
- Cold weather: Propane generators generally start more easily in cold temperatures, as propane remains in a gaseous state. Gas can be more difficult to vaporize in cold weather, making starting harder.
- Hot weather: Both types perform well in hot weather, but gas generators may be slightly more efficient in high temperatures.
- High altitude: Propane generators typically perform better at high altitudes due to the lower air pressure, which affects the air-fuel mixture less than in gas engines.
Consider your local climate when choosing between propane and gas generators for optimal performance.
How much propane do I need to power my house during an outage?
Homeowners need a 500-gallon propane tank for continuous backup power. Your generator consumes 2-3 gallons per hour at half load. A full tank provides several days of emergency power.
What happens if my propane generator runs out of fuel while operating?
The generator stops immediately when propane runs out. This differs from gasoline generators’ gradual shutdown. Users should monitor fuel levels regularly. Operators must check tank connections before each use.
Can I convert my existing gasoline generator to run on propane?
Qualified technicians can convert most gasoline generators to propane operation. The conversion requires specialized kits. Homeowners should seek professional installation for safety.
How do I maintain proper ventilation for my propane generator?
Operators must place generators twenty feet from buildings. The exhaust should point away from structures. Homeowners should maintain clear space around units. Proper placement prevents carbon monoxide dangers.
What size propane tank should I get for my portable generator?
Portable generators work best with 20-30 pound tanks. These tanks deliver 4-6 hours of power at half load. Users can transport these tanks easily. Standard 5000-watt generators operate efficiently with these sizes.
Does altitude affect propane generator performance?
High altitudes reduce generator power by 3.5% per thousand feet. Users should increase generator size by 20% at elevation. Mountains affect propane combustion efficiency. Installers must adjust generators for altitude operation.
What’s the difference in maintenance requirements between propane and gas generators?
Propane systems need fewer maintenance checks. Owners must inspect regulators monthly. Technicians should check fuel lines seasonally. Clean-burning propane prevents carburetor buildup.
Can I run my propane generator in the rain?
Users must protect generators from direct rainfall. Generator tents provide essential coverage. The unit requires proper ventilation during operation. Weather protection ensures safe generator function.

Leave a Reply