As power outages and off-grid living have become increasingly common, portable power solutions have gained significant importance. Two popular options for backup power are solar generators and gas generators. This article will provide a detailed comparison of these two technologies, helping you decide based on your needs.
Understanding Solar Generators
Solar generators harness the sun’s power to generate electricity. These portable power stations consist of solar panels, a battery, and an inverter. They convert sunlight into electrical energy, which is then stored in the battery for later use.
The potential of solar generators to transform off-grid living is substantial. As explored in our article on how solar generators can revolutionize off-grid living, these devices offer a sustainable and independent power solution for those seeking to live away from traditional power grids.
Advantages of Solar Generators
Solar generators offer several compelling benefits that make them an attractive option for many users:
- Clean Energy: One of the most significant advantages of solar generators is their environmental friendliness. They produce zero emissions during operation, making them an excellent choice for those concerned about their carbon footprint. This clean energy production aligns well with global efforts to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and combat climate change.
- Silent Operation: Solar generators operate near silence, unlike their gas-powered counterparts. This quiet operation makes them ideal for use in noise-sensitive environments such as campgrounds, residential areas, or during outdoor events where noise pollution could be a concern.
- Low Maintenance: Solar generators’ core components do not have moving parts, significantly reducing the need for regular maintenance. This low-maintenance nature saves time and reduces long-term costs associated with upkeep and repairs.
- Renewable Energy Source: Solar generators can continue to produce power as long as there is sunlight. This renewable aspect provides a sense of energy independence and reliability, especially in remote locations where fuel resupply might be challenging.
- Indoor Safe: The absence of fuel combustion means solar generators can be safely used indoors without the risk of harmful fumes or carbon monoxide poisoning. This indoor safety feature makes them versatile for various applications, from home backup power to indoor workspaces.
Disadvantages of Solar Generators
While solar generators offer many benefits, they also have some limitations to consider:
- Weather Dependent: Solar generators’ efficiency can be significantly reduced in cloudy or rainy conditions. This dependency on favorable weather can be a drawback in regions with frequent overcast skies or during seasons with limited sunlight.
- Higher Initial Cost: The upfront investment for a solar generator is typically higher than that of a comparable gas generator. This higher initial cost can be a barrier for some consumers, although it’s often offset by lower operating costs over time.
- Lower Power Output: Solar generators generally have less power capacity than gas generators of similar size. This lower output might limit their ability to power high-wattage appliances or multiple devices simultaneously.
Understanding Gas Generators
Gas generators use fossil fuels like gasoline, propane, or diesel to produce electricity. They consist of an engine that powers an alternator to generate electrical current. Due to their reliability and high power output, gas generators have been a staple in the portable power market for decades.
Advantages of Gas Generators
Gas generators offer several advantages that make them a popular choice for many applications:
- High Power Output: One of the most significant advantages of gas generators is their ability to produce high levels of electricity. They can generate more power than most solar generators, making them suitable for powering larger appliances, tools, or even entire households during outages. This high output capacity is particularly valuable when substantial power is needed quickly, such as in emergency response scenarios or on construction sites.
- Consistent Power: Unlike solar generators, gas generators’ performance is not dependent on weather conditions. They can provide a steady stream of electricity regardless of whether it’s sunny, cloudy, or nighttime. This consistency makes them reliable for critical applications where uninterrupted power is essential.
- Lower Initial Cost: Gas generators of comparable power output are generally less expensive to purchase than solar generators. This lower upfront cost can make them more accessible to a broader range of consumers, especially those who need a backup power solution but have a limited budget.
- Quick Refueling: Gas generators can be refilled quickly, allowing for continuous operation with minimal downtime. This quick turnaround is particularly advantageous when extended power is needed, such as during prolonged outages or events lasting several days.
Disadvantages of Gas Generators
Despite their advantages, gas generators come with several drawbacks that are important to consider:
- Noise Pollution: Gas generators can be quite loud during operation, with noise levels often exceeding 70 decibels. This noise can be disruptive in residential areas and may not be suitable for use in noise-sensitive environments or during nighttime hours.
- Emissions: Gas generators that burn fossil fuels produce exhaust fumes, including carbon monoxide, making them unsuitable for indoor use. These emissions contribute to air pollution and can be harmful if not properly ventilated, limiting the generator’s versatility and posing potential health risks.
- Ongoing Fuel Costs: While gas generators may have a lower initial cost, they require regular fuel purchases to operate. These ongoing fuel costs can add up over time, especially with frequent use or during periods of high fuel prices.
- Maintenance Needs: Regular engine maintenance is necessary to keep gas generators running efficiently and to extend their lifespan. This maintenance includes oil changes, filter replacements, and periodic tune-ups, which add to the overall cost and time investment of owning a gas generator.
Comparing Key Factors
When deciding between solar and gas generators, several key factors come into play:
Power Output
Gas generators typically offer higher power output, ranging from 2,000 to 20,000 watts or more. This high output makes them capable of simultaneously powering entire homes or multiple high-wattage appliances. Solar generators usually provide between 1,000 to 3,000 watts, with some high-end models reaching up to 5,000 watts. While this output is sufficient for many applications, it may limit the ability to power larger appliances or multiple devices at once.
Portability
Solar generators are generally lighter and more portable than their gas counterparts. Most solar generators weigh between 30 to 100 pounds, making them relatively easy to transport. Gas generators, especially those with higher power outputs, can be quite heavy, often weighing 100 pounds or more. This weight difference can be a significant factor for users who need to move their generator frequently or use it in remote locations.
Runtime and Fuel Efficiency
Solar generators can provide indefinite runtime as long as there’s sunlight to recharge the battery. This continuous operation capability is particularly advantageous for long-term use in remote locations or during extended power outages. Gas generators are limited by their fuel tank capacity and efficiency, typically running for 8-12 hours on a full tank. While they can be refueled for continued use, this requires a steady supply of fuel, which may not always be readily available.
Environmental Impact
Solar generators have a minimal environmental footprint, producing clean energy with no direct emissions during operation. This eco-friendly nature aligns with growing environmental concerns and regulations. On the other hand, gas generators burn fossil fuels, contributing to air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. The environmental impact of gas generators extends beyond their use, including the extraction and transportation of the fuel they consume.
Cost Considerations
While solar generators have a higher upfront cost, they have minimal ongoing expenses, primarily limited to potential battery replacements every few years. Gas generators are cheaper initially but incur regular fuel and maintenance costs. Over time, the total cost of ownership for a gas generator can exceed that of a solar generator, especially with frequent use or in areas with high fuel prices.
Choosing the Right Generator for Your Needs
The choice between a solar and gas generator ultimately depends on your power needs, budget, and environmental considerations. Here are some scenarios to consider:
For Camping and Outdoor Activities
Solar generators are often preferred for camping and outdoor activities due to their portability, silent operation, and eco-friendliness. They’re ideal for powering small devices, lights, and light camping equipment. The ability to recharge using solar panels makes them well-suited for extended trips in remote areas where fuel resupply might be challenging.
For Home Backup Power
Due to their higher output, gas generators are typically more suitable for whole-house backup power. They can handle the power demands of essential home appliances like refrigerators, air conditioners, and water heaters. However, solar generators are gaining ground in this area, especially for powering essential appliances during short outages. Some homeowners opt for a hybrid approach, using a solar generator for daily backup and a gas generator for extended outages or high-power needs.
For RV and Van Life
Solar generators are becoming increasingly popular in the RV and van life communities. They provide a sustainable power source without the noise and fumes associated with gas generators, which is particularly important in the confined spaces of RVs and vans. The ability to recharge while driving or parked makes them an excellent fit for this mobile lifestyle.
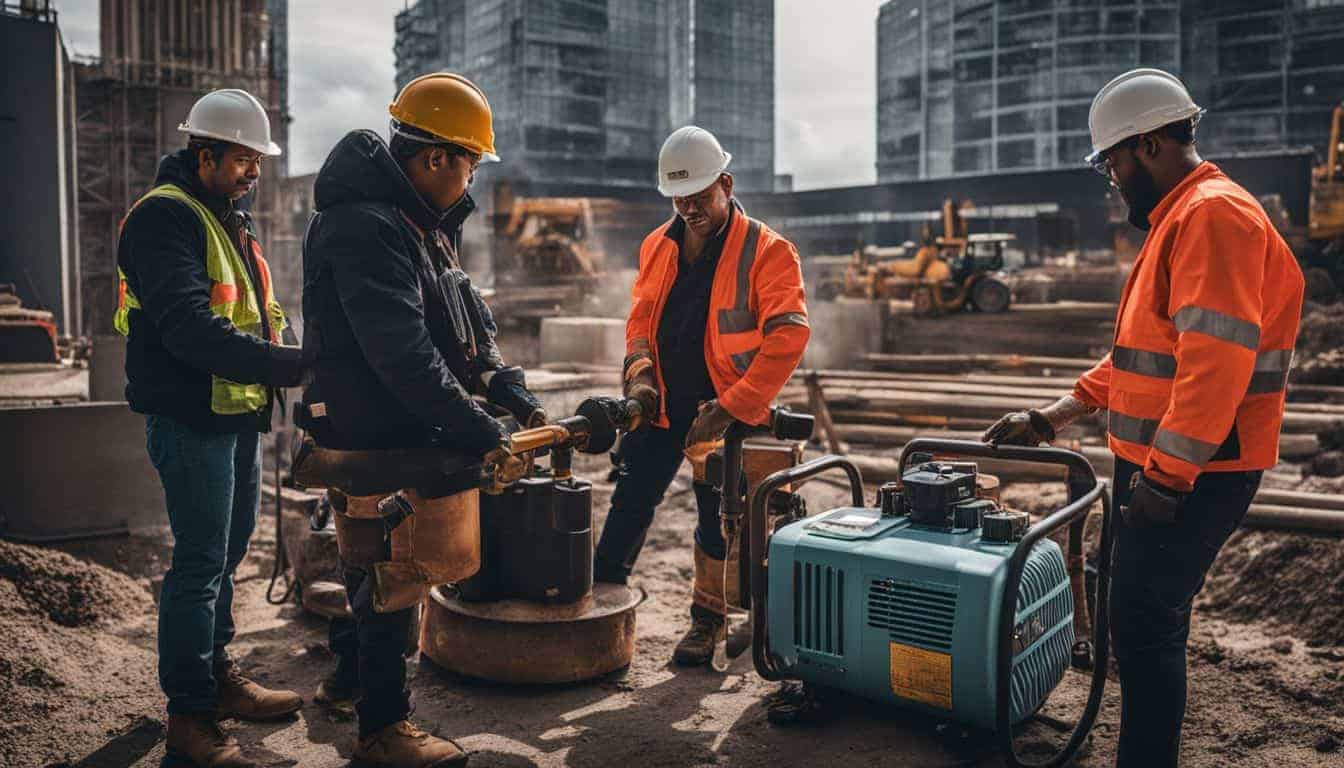
For Construction Sites
Gas generators remain the go-to choice for construction sites due to their high power output and ability to run continuously with quick refueling. They can power multiple high-wattage tools and equipment simultaneously, essential for maintaining productivity on job sites.
Future Trends
The portable power industry is rapidly evolving, with both solar and gas generator technologies seeing significant advancements:
- Solar generator technology is advancing, improving solar panel efficiency and battery storage capacity. We’re seeing the development of more powerful and compact solar generators capable of rivaling traditional gas generators in output.
- Gas generators are becoming more fuel-efficient and less polluting. Manufacturers focus on developing cleaner-burning engines and incorporating advanced emission control technologies to meet stricter environmental regulations.
- Hybrid systems that combine solar and gas technologies are emerging, offering the benefits of both worlds. These systems use solar power as the primary source and gas as a backup, providing a reliable and eco-friendly power solution that can adapt to various conditions and power needs.
Maintenance Considerations
Proper maintenance is crucial for ensuring the longevity and efficiency of both solar and gas generators. For gas generators, regular maintenance tasks include oil changes, air filter replacements, and spark plug checks. Our guide on generator maintenance provides detailed information on keeping your gas generator in top condition.
While solar generators generally require less maintenance, they still benefit from proper care. Important tasks include regularly cleaning solar panels, checking battery health, and ensuring all connections are secure. For more specific advice, our article on solar generator maintenance tips and best practices offers valuable insights.

Conclusion
Both solar and gas generators have their place in the portable power market. Your choice should depend on your power needs, budget, and environmental considerations. Solar generators excel when clean, quiet operation is paramount, and power needs are moderate. They’re ideal for camping, RV use, and as a supplement to home power systems. Gas generators remain the top choice for high-power applications and situations requiring consistent output regardless of weather conditions, such as construction sites or whole-house backup power.
As technology advances, we can expect to see further improvements in both types of generators, making portable power solutions even more efficient and accessible. The question of whether solar generators can power an entire house is becoming increasingly relevant as their capacity grows.
Leave a Reply